The Earth is a fascinating planet that has been around for billions of years, but when was the Earth formed? This is an interesting question that has puzzled scientists for centuries. It is believed that the Earth was formed about 4.5 billion years ago. Through the use of radiometric dating and other scientific methods, scientists have been able to determine that the Earth is approximately 4.5 billion years old. This article will discuss the evidence and theories that have been used to determine when the Earth was formed, and how this knowledge has impacted our understanding of the universe. On the same topic, visit facts about earths crust.
Unveiling the Secrets of Earth’s Formation
Earth is a fascinating and mysterious place. It has been studied and explored for centuries, yet its secrets remain to be unlocked. From its formation, composition, and evolution, the mysteries of Earth are slowly being unraveled. In this article, we will explore the secrets of Earth’s formation and discuss the various theories that have been proposed to explain its evolution.
Earth’s formation began 4.6 billion years ago when the solar system was created. It is believed that the planets formed from the same cloud of dust and gas that formed the Sun. This cloud, known as the solar nebula, was composed of hydrogen and helium and was heated by the young Sun. As the nebula cooled, it began to collapse under its own gravity, and dust particles merged together. These particles grew larger and larger until they formed small clumps called planetesimals. Over time, these planetesimals collided with each other, and the heat of their collisions melted the rock and created the planets.
It is believed that Earth was formed from a process called accretion. This process involves the growth of planetesimals and the formation of larger and larger bodies. During this process, the planetesimals collided and merged together, forming the Earth. It is believed that the Earth’s core was formed first, followed by a molten layer, and then the crust.
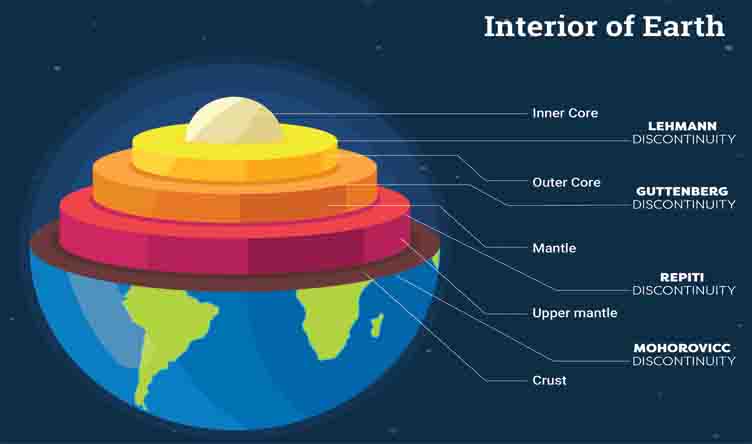
The Earth’s composition is also an interesting mystery. It is composed mostly of silicate minerals, iron, nickel, and oxygen. The Earth’s core is believed to be composed of iron and nickel, while the mantle is composed of silicate minerals. The crust is composed of the same silicate minerals, but with a much lower concentration of iron and nickel.
The evolution of Earth is a complex process that is still being studied. It is believed that Earth’s early environment was very different from today. It is believed that the Earth was much hotter, and that there were more active volcanoes and more frequent meteorite impacts. As the Earth cooled, the atmosphere and oceans formed, and the climate changed. Over time, the climate has become more stable, and the Earth has evolved into the planet we see today.
The secrets of Earth’s formation are slowly being unraveled, but much remains to be discovered. Understanding how Earth formed and evolved is key to understanding our own history and the history of life on Earth. We can only hope that further research and exploration will uncover more of the mysteries of our wonderful planet.
Exploring the Age of the Earth
The age of the Earth has been the subject of much debate and controversy for centuries. In fact, the concept of a young Earth was a cornerstone of the Catholic Church for centuries, challenging scientists who believed that the Earth was much older than the Church claimed. In recent years, however, the age of the Earth has been determined with greater certainty, and the scientific consensus is that the Earth is approximately 4.5 billion years old.
This conclusion is based on a wide range of evidence gathered from numerous sources. First, scientists have used radiometric dating techniques to measure the age of rocks and minerals, which gives us a fairly accurate estimate of the age of the Earth. In addition, scientists have examined the fossil record to determine the age of life on Earth. By comparing what is known about the fossil record to the radiometric age estimates, scientists are able to deduce an approximate age for the Earth.
In addition, scientists have used astronomical evidence to estimate the age of the Earth. For example, by studying the orbits of planets, astronomers have determined that the solar system is approximately 4.6 billion years old. Similarly, by observing the rate of star formation in the universe, astronomers have determined that the universe is at least 13.8 billion years old. This indicates that the Earth is significantly older than the age of the universe, which is in line with the scientific consensus.
In conclusion, the age of the Earth is estimated to be approximately 4.5 billion years old, based on a range of evidence gathered from a variety of sources. This age has been confirmed by radiometric dating techniques, the fossil record, and astronomical evidence. The scientific consensus is that the Earth is significantly older than the age of the universe, which is estimated to be at least 13.8 billion years old.
The Fascinating Story of Earth’s Origin
Earth’s origin is a captivating story that has been the source of much fascination and speculation. For centuries, scientists have sought to unravel the mysteries of our planet’s genesis, and over time, our understanding of the Earth’s creation has grown.
The formation of the Earth began approximately 4.5 billion years ago with the coalescence of the solar system from a nebula of dust and gas. As the matter in the nebula grew denser and hotter, gravity began to take hold, forming the planets of our solar system, including Earth.
During the first 500 million years, the Earth was still in its infancy, with its surface a mass of molten rock and lava, and its atmosphere made up of gaseous elements such as hydrogen, helium, methane, and ammonia. As the planet cooled, a solid crust formed, and water vapor and other compounds began to accumulate, creating the Earth’s early oceans.
The next stage of the Earth’s formation was the creation of the earliest forms of life. Scientists believe that these organisms first began to emerge in the oceans some 3.5 billion years ago, and over time, they evolved into the complex lifeforms we see today.
As the Earth has developed, its atmosphere and climate have also changed. Over the past several million years, the Earth’s landmasses have shifted and the global climate has fluctuated, with ice ages and periods of warming.
Today, the Earth is a dynamic and ever-changing place. While the details of our planet’s origin story may remain shrouded in mystery, its history is an incredible reminder of the power of nature and its ability to shape our world.
